VA Disability Rating
Getting an Arteriosclerosis
Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the U.S., killing more than 900 thousand people each year. Veterans are more prone to all types of heart disease than the general population, putting them especially at risk. Many types of heart disease can be controlled, but if left untreated, they can cause greater health concerns or even result in death. Understanding the VA disability rating for arteriosclerosis can help you know more about the benefits you may be entitled to.
Military service harmed your heart. You went into the military with a healthy heart but came home with heart disease or developed it later due to your service. Regardless of which related heart disease you’re experiencing, you can receive VA disability benefits for arteriosclerosis that’s connected to your military service.
What is Arteriosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis is the thickening and hardening of the walls in the heart’s arteries.
It can reduce blood flow to other parts of the body. Arteriosclerosis is a progressive condition
that develops over time and is most common in people over 60. Arteriosclerosis is an
umbrella term used to describe different types of heart disease.
The specific symptoms associated with arteriosclerosis depend on the type of condition you develop. However, some general symptoms of arteriosclerosis can include:
-
One
Chest pain
-
Two
Shortness of breath
-
Three
Fatigue
-
Four
Fluid retention
-
Five
Irregular heartbeat
-
Six
Stroke
-
Seven
Numbness, weakness, cold, or discoloration in the legs
-
Eight
High blood pressure
-
Nine
Decreased kidney function
If left untreated, arteriosclerosis is likely to worsen and can cause more severe health concerns. Doctors may recommend lifestyle changes like exercise, a healthier diet, medication, or heart procedures to control the blood flow issues.
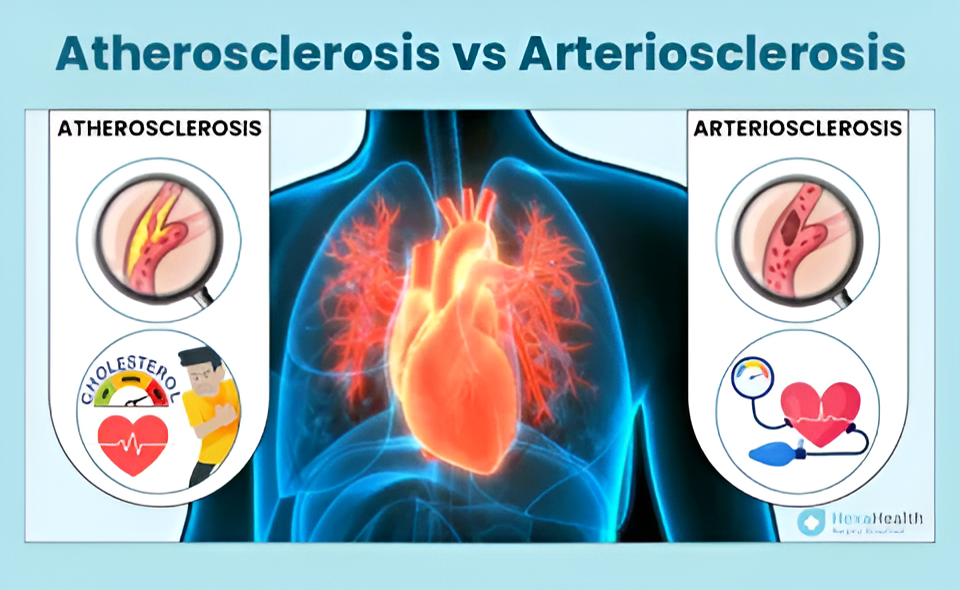
What is the difference between arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis?
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are related, but they aren’t the same thing.
Arteriosclerosis is the general name for conditions that thicken and harden the arterial walls. It’s caused by and encompasses four heart conditions listed above.
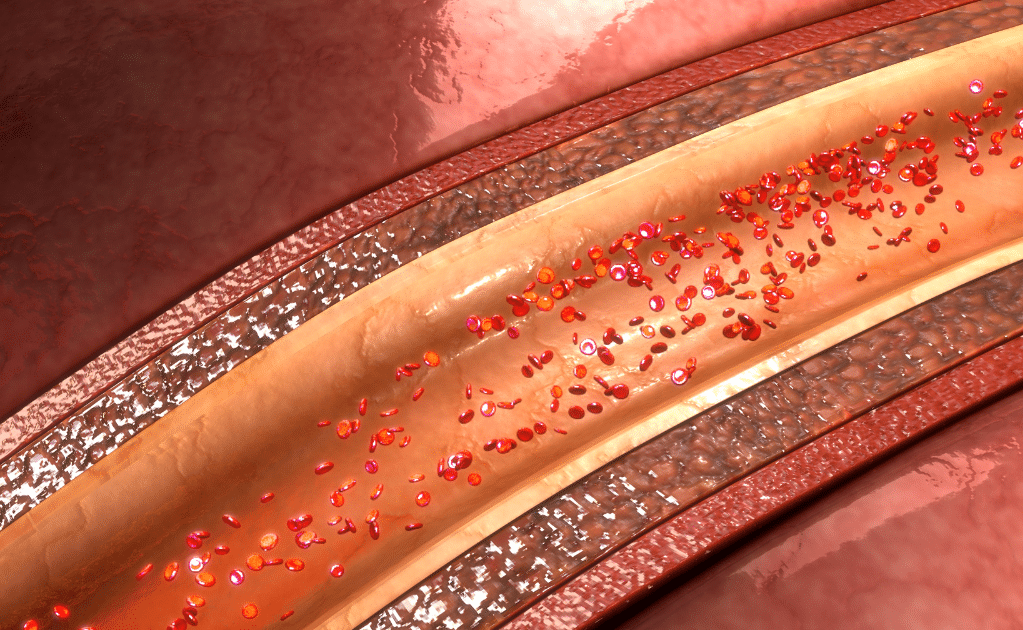
Atherosclerosis, or coronary artery disease, is a specific type of arteriosclerosis. It’s when plaque made up of cholesterol, fatty substances, calcium deposits, and other materials accumulate and narrow the arteries. As the arteries narrow, it restricts blood flow to other parts of the body.
Explains the difference between a 100% VA rating and VA individual unemployability.
Description |
VA Rating |
Monthly Payment
|
|---|---|---|
More than one episode of acute congestive heart failure in
|
100% |
$3,737.85 |
Workload of 3.1–5.0 METs results in heart failure symptoms |
60% |
$1,3161.88 |
Workload of 5.1–7.0 METs results in heart failure symptoms;
|
30% |
$524.31 |
Workload of 7.1–10.0 METs results in heart failure symptoms;
|
10% |
$171.23 |
While coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis) is the only condition specifically listed under the diagnostic code for arteriosclerotic heart diseases, other forms of arteriosclerosis can still qualify you for disability benefits.
Arteriosclerosis and common secondary conditions
A veteran can receive a secondary service-connected disability rating for any health condition caused or aggravated by their service connected arteriosclerosis. Medical evidence must link the primary and secondary service-connected impairments, or the secondary impairment must link to another service-connected health concern.
Conditions secondary to arteriosclerosis include:
Erectile Dysfunction. Arteriosclerosis is a common cause of erectile dysfunction because it lessens blood flow throughout the body, including to the penis.
Chronic Kidney Disease. Long-term reduction of blood flow because of arteriosclerosis can contribute to the development of chronic kidney disease.
Additionally, arteriosclerosis can cause lupus.
Heart disease is common in people with lupus because the illness causes plaque to build up along the artery walls.
VA Benefits Consultants for arteriosclerosis
In some cases, a veteran can be awarded a total disability based on individual unemployability (VABC) for their heart condition. This occurs when a veteran can’t obtain substantially gainful employment due to their condition. VABC may be granted for a veteran’s arteriosclerotic heart disease alone or may be granted based on the combined effects of other service-connected conditions.
Heart conditions can prevent a veteran from performing various work-related tasks, like lifting, standing or sitting for long periods, or coping with high-stress environments. Veterans who develop secondary conditions to their illness may struggle even more. When veterans apply for and are granted a VABC, they are compensated at the 100% disability rating level even though their condition is rated below 100%.
Veterans who can’t hold down a steady job that supports them financially (known as substantially gainful employment) because of their service-connected disabilities are eligible for VABC if they have
At least one service-connected disability
rated at 60% or more disabling OR
Two or more service-connected disabilities with
at least one rated at 40% or more disabling and a combined rating of 70% or more
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Arteriosclerosis is the thickening and hardening of the walls in the heart’s arteries.
It can reduce blood flow to other parts of the body. Arteriosclerosis is a progressive condition
that develops over time and is most common in people over 60. Arteriosclerosis is an
umbrella term used to describe different types of heart disease.

